The Bar Magnet
The Bar Magnet: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Magnetism, Bar Magnet, Bar Magnet as an Equivalent Solenoid, Magnetic Field Lines of a Bar Magnet, Magnetic Monopole, Pole Strength, Neutral Points and, Magnetic Dipole Moment of a Bar Magnet
Important Questions on The Bar Magnet
The length of a magnet is large compared to its width and breadth. The time period of its oscillation in a vibration magnetometer is . The magnet is cut perpendicular to its length into three equal parts and three parts are then placed on each other with their like poles together. The time period of this combination (in ) will be
What is the force between two magnetic dipoles?
The length of a magnet is large compared to its width and breadth. The time period of its oscillation in a vibration magnetometer is . The magnet is cut along its length into three equal parts and three parts are then placed on each other with their like poles together. The time period of this combination (in ) will be
An electron moves in a circular orbit with a uniform speed It produces a magnetic field at the centre of the circle. The radius of the circle is proportional to :
The ratio of magnitude of magnetic field at a distance from short bar magnet in longitudinal direction to the field at distance in transverse direction is
A magnetic needle of magnetic moment and moment of inertia is performing simple harmonic oscillations in a magnetic field of Time taken for complete oscillations is :
Two lines of force due to a bar magnet:
A bar magnet of length has a point and along axis at a distance of and on the opposite ends. Ratio of magnetic fields at these points will be
The effect on a freely suspended magnetic needle due to a uniform magnetic field is as follow.
The magnetic moment of a bar magnet is . Its pole strength is . Its magnetic length is
A magnet makes oscillations per minute at a place having earth's horizontal magnetic field intensity of . At another place, it takes to complete one vibration. The value of earth's horizontal field at that place is
The areas of cross-sections of three magnets of same length are and respectively. The ratio of their magnetic moments will be
A magnetic dipole is acted upon by two magnetic fields which are inclined to each other at an angle of . One of the fields has a magnitude of . The dipole attains stable equilibrium at an angle of with this field. The magnitude of the other field (in mT) is close to:
When a bar magnet is broke into different pieces, each piece is a complete magnet.
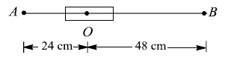
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards the south. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is .
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards the east. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is .
